Module
(2) Loops and Condition in MATLAB and Excel
1. Logical and Relational Operations in MATLAB
Suppose that you
have two arrays A and B, and you want to test the relationship between them, So
you can check this by using some logical operators such as (>, <,=,
~,&,|). If the Condition is matched, it will (1) or give (0).
Let's test the following
commands:
|
< |
Smaller
Than |
|
> |
Greater
than |
|
= |
Equal |
|
~ |
Not
equal |
|
& |
And |
|
| |
OR |
>
A=[1 2 3 4 5]
A
=1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00 5.00
>>
B=[2 1 5 4 -1]
B
= 2.00 1.00 5.00 4.00 -1.00
>> A>B
ans
= 1×5 logical array
0 1
0 0 1
>> A>=B
ans
=1×5 logical array
0 1
0 1 1
>> A<B
ans
= 1×5 logical array
1 0
1 0 0
>> A==B
ans
=1×5 logical array
0 0
0 1 0
>> A~=B
ans
=1×5 logical array
1 1 1
0 1
2. Creating a script in MATLAB using M.Files
You can write a series
of statements in M.file to run all at once by CTR+N or New Script.
M files can be a
script file or function file.
In a script file, a
series of MATLAB commands can be executed at once either by typing the saved
file name in the command window or by select Run.
You can perform the
logical and relational operations in MATLAB using M.Files. Let us try it. In a
new script file, write the following codes and save it as Untitled, then;
in the command window, type Untitled or select Run
Example
Create a
script Insert students grades and find who got A
Function (find)
It is used to locate
the nonzero elements in a vector or a matrix.
Example 1
Create a
script file where students' grades can be inserted in a vector.
Show the
students' grade who got (A) (i.e. >=90) and their location in the vector.
Example 2
Create a
script file in which you can insert car speeds and catches those speed >=80.
Example 3
Create M file
to list values of X and Y in a proper table and plot them
__________
Function (tic&toc)
tic and toc are used
to calculate the elapsed time between them
Example
Create M file
to Program a Timer Alarm in seconds
clc; clear;
disp('This program is a timer Alarm/ by Ahmed Elkhatat');
disp('_______________________________')
n=input('Set the timer in seconds: ');
tic;
beep;
pause
(n);
beep;
toc;
msgbox('Time is up')
3. Creating Function files in MATLAB using M.Files
Function: are files
that take certain inputs and execute sequence of steps, and then returns
outputs at the end.
Function files has
different forms, and their syntax can be presented as following:
function output= function_name (input
1, input 2,..)
function [out 1, out2,..]
= function_name (input 1, input 2,..)
function [out 1, out2,..]=
function_name
function function_name (input
1, input 2,..)
function function_name
Example 1:
Create a
function to find the area of a triangle when its height and base are given.
Note (1) :
You can use % to add comments to
your script. This will be very helpful as you can recall these comments if you write
the command help (function
name)
Note (2):
When You save the function, make
sure that the file name is precisely the function name to execute
the function correctly.
Example 2
Create a
function to calculate the velocity of a free-falling bungee jumper, where the the velocity of a free-falling bungee jumper is defined as
Where:
Ø
v is the velocity in
m/s
Ø
g is the
acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s2)
Ø
m is mass in kg
Ø
Cd is the drag the coefficient in kg/m
Ø
t is time in sec
If you want to
create a function without an output (i.e., to assign the output later as a display the message, then you can write the function in this form
function function_name (input 1, input 2,..)
function
bungeevel1(m,t,cd);
Create a
function to calculate the loss coefficient and head loss of a pipe when friction
factor, pipe length, pipe diameter, and fluid velocity are given
Where:
Ø
v is velocity in
m/s
Ø
g is the
acceleration due to gravity (9.81 m/s2)
Ø
f the friction
factor (fanning)
Ø
L is the pipe
length (m)
Ø
D is the pipe
diameter (m)
Ø
Kf is the loss
coeffient
Ø
HL is the head
loss (m)
Note that you got only one value, so in order to get the other values, the function
should be written as
Another way
to create the function file using
function function_name (input 1, input 2,..)
4. Loops and Conditions using (If expression) in MATLAB.
If expression, statements,
end evaluates an expression and
executes a group of statements when the expression is true. An expression is
true when it is nonempty and contains only nonzero elements (logical or real numeric).
Otherwise, the expression is false.
Syntax
|
if
expression statements end |
if
expression else statements end
|
if
expression statements elseif
expression statements else statements end
|
Example 1:
Create M file
to calculate the Body Mass Index (BMI) and inform the user what the index means
using (if Condition) in a function file.
Note:
Ø
BMI <18.5,
then it is Underweight Body
Ø
18.5 < BMI
< 24.9, them it is Normal Body
Ø
24.9 < BMI
< 29.9 it is Overweight Body
Ø
BMI > 29.9,
then it is Obese Body
Try
it using (if/ ifelse)
Example 2:
Create M file
to show a student's name and show his Graded letter using input function and
(if Condition). (Inputs is name, %, and Course Code)
__________
Example 3:
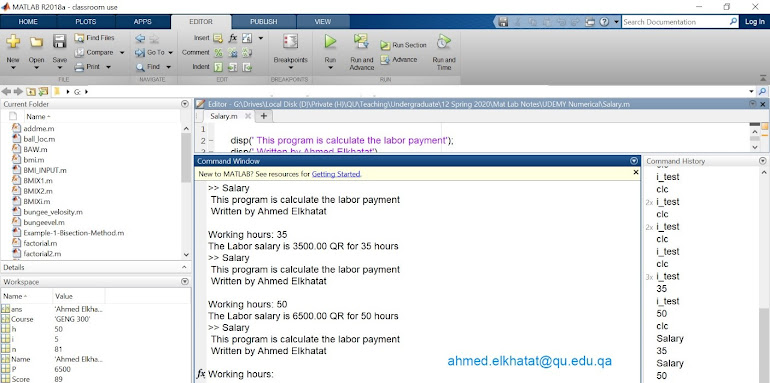
Create M file
to calculate the labor payment according to the following rules.
100 QR/hr for the
first 35 hrs.
150 QR/hr for the
next 25 hrs.
200 Qr/hr for further
hrs.
Example 4:
Create M file
to calculate the Calculate a series of students Grade letters using (Students'
Scores should be inserts as an array.
5.
Loops and Conditions using (For
expression) in MATLAB.
For loop is used
to repeat a specified number of times
Syntax
for index =
values
statements
end
Example 1:
Example 2:
Example 3:
Note: if you
want the MATLAB only to show the last value, then get disp(x) out of the loop
as following
Example 4:
Use
a For loop to calculate the factorial number.
6.
Loops and Conditions using (While
expression) in MATLAB.
While loop is used
to repeat when Condition is true.
Syntax
while expression
statements
end
Example 1:
Use while loop
to calculate the factorial number.
Practice the following
Create if loop file where one can insert his blood
pressure. A message telling him about
his health status is as follows:
1)
Low blood
pressure (hypotension): If the top
number (systolic) is lower than 90 mm Hg
or the bottom number (diastolic) is lower than 60 mm Hg
2)
High blood
pressure (hypertension): If the top number (systolic) is higher than 120 mm Hg or the bottom number
(diastolic) is higher than 80 mm Hg
3)
Normal blood
pressure: If the top number (systolic) is between (90-120) mm Hg or the bottom
number (diastolic) is between (60-80) mm Hg
7. IF Condition using in Excel
The most straightforward formula of (IF) Condition in
EXCEL is
IF(logical test, value if true, value if false)
Example
For the following
given data, if the value is less than 60, then show Fail, if not do nothing
Note that we put Fail between two double quotes because
it's text, not value. Also the false option, we put two empty double quotes ("")
to do nothing. For not equal Condition you can use <>
Example
In the same example,
if the value is less than 60, then show Fail. If it is less than 70, show D. If
it is less than 80, then show C, Less than 90, then show B, else show A.
In this Condition, we replace the (false value) with the
new conditional as follows:
For more complicated logical tests, (and) (or) can be
used as following
IF(and(logical test_1, logical test_2),value if true, value
if false)
IF(or(logical test_1, logical test_2),value if true, value
if false)
Example
A military college put
height and weight standards for accepting new students as following (Height
160-185 Kg) and (weight 55-80 Kg). Applicants out of these ranges should be rejected.
|
Student
ID |
Height
(cm) |
Weight
(Kg) |
|
1698 |
182 |
102 |
|
1687 |
160 |
70 |
|
3134 |
181 |
110 |
|
1357 |
171 |
64 |
|
3776 |
180 |
60 |
|
1897 |
157 |
105 |
|
1712 |
163 |
116 |
|
1435 |
177 |
73 |
|
4448 |
184 |
80 |
|
3413 |
170 |
110 |
If you want to color the Accepted cells in green and the
rejected cells in red, then
a)
Select the
Colum you want to apply the conditional formatting.
b)
In the Home
tab, select Conditional Formatting, from the drop list, select New
Rule, as shown below
In the New Formatting Rule window
a)
Rule Type: Select
Format only cells that contain.
b)
Edit the Rule
Description: Format only cells with Specific Text and type the word or
select the cell that contains the word (Rejected), then select Format.
c)
In the Format
Cells window Select Fill, Choose the color, then OK
d)
Repeat the same
steps to color "Accepted in Green."
End of
this section







































No comments:
Post a Comment